Polyethylene (PE) pipes, including High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Medium-Density Polyethylene (MDPE), and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), are at the heart of many critical infrastructure systems worldwide. These pipes offer unparalleled durability, corrosion resistance, and recyclability, making them a top choice for industries such as water supply, sewage, gas distribution, and industrial applications. As global demand for PE pipes continues to rise, driven by their outstanding properties, the industry is under increasing pressure to improve the efficiency, sustainability, and environmental impact of the manufacturing process. This article highlights the latest innovations and best practices for optimal performance, energy efficiency, and sustainability in PE pipe extrusion machinery.
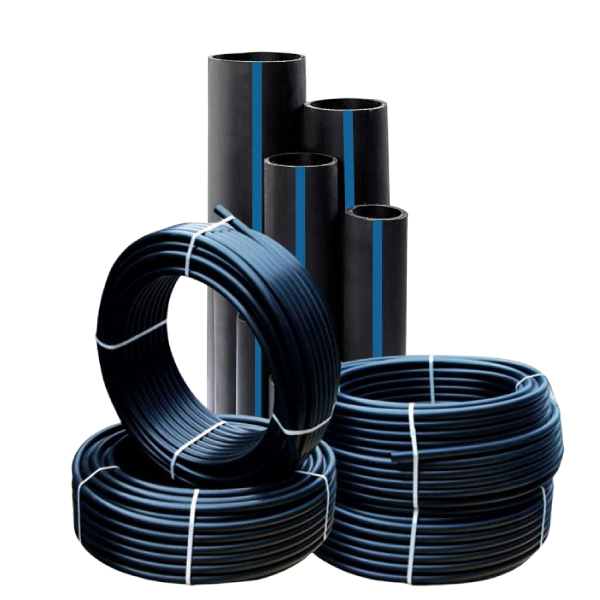

1-Technological Innovations in PE Pipe Extrusion Machinery
Modern PE pipe extrusion lines have evolved significantly over the last five years, introducing advanced technologies aimed at increasing performance while reducing environmental impact. Among the most notable advancements are:
• Energy Efficiency: One of the most significant improvements in PE pipe extrusion has been in energy efficiency. Extrusion lines now incorporate IE5+ permanent-magnet synchronous motors that deliver up to 18% energy savings compared to older motor technologies. Short-wave infrared die heaters have also become standard, enabling faster heat-up times (up to 70% faster) while reducing energy consumption by 40%. Additionally, heat recovery systems capture waste heat from the extrusion process to pre-heat materials, further enhancing energy efficiency. As a result, leading-edge machines now operate at energy consumption rates as low as 0.18 kWh/kg, setting a new benchmark for sustainability in the industry.
• Multi-Layer Co-Extrusion: The ability to produce multi-layer pipes has revolutionized PE pipe production. Co-extrusion technology allows for the creation of pipes with different material layers that enhance performance characteristics. For example, pipes with an oxygen barrier layer (EVOH) or reinforced with glass fibers provide increased strength and resistance to external environmental factors, making them ideal for demanding applications like district heating systems. These innovations allow manufacturers to customize pipe properties, leading to improved durability and functionality.
• Large-Diameter Pipe Production: The growing demand for larger diameter pipes (over 1600 mm) for infrastructure projects has led to the development of advanced extrusion lines capable of producing large-diameter PE pipes with diameters up to 2600 mm. These lines employ twin- and triple-extruder configurations and incorporate vacuum-assisted internal cooling towers to expedite cooling times and increase production speed. Fully automated systems now handle the stacking and arrangement of these large pipes, reducing labor costs and improving operational safety.
• Industry 4.0 Integration: The PE pipe extrusion industry is embracing smart manufacturing technologies. The integration of IoT sensors, real-time monitoring systems, and predictive maintenance technologies helps optimize operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Full-line OEE (Overall Equipment Efficiency) dashboards enable manufacturers to identify and resolve bottlenecks, while AI-driven predictive maintenance systems use data from sensors to forecast potential machine failures before they occur, minimizing disruption.
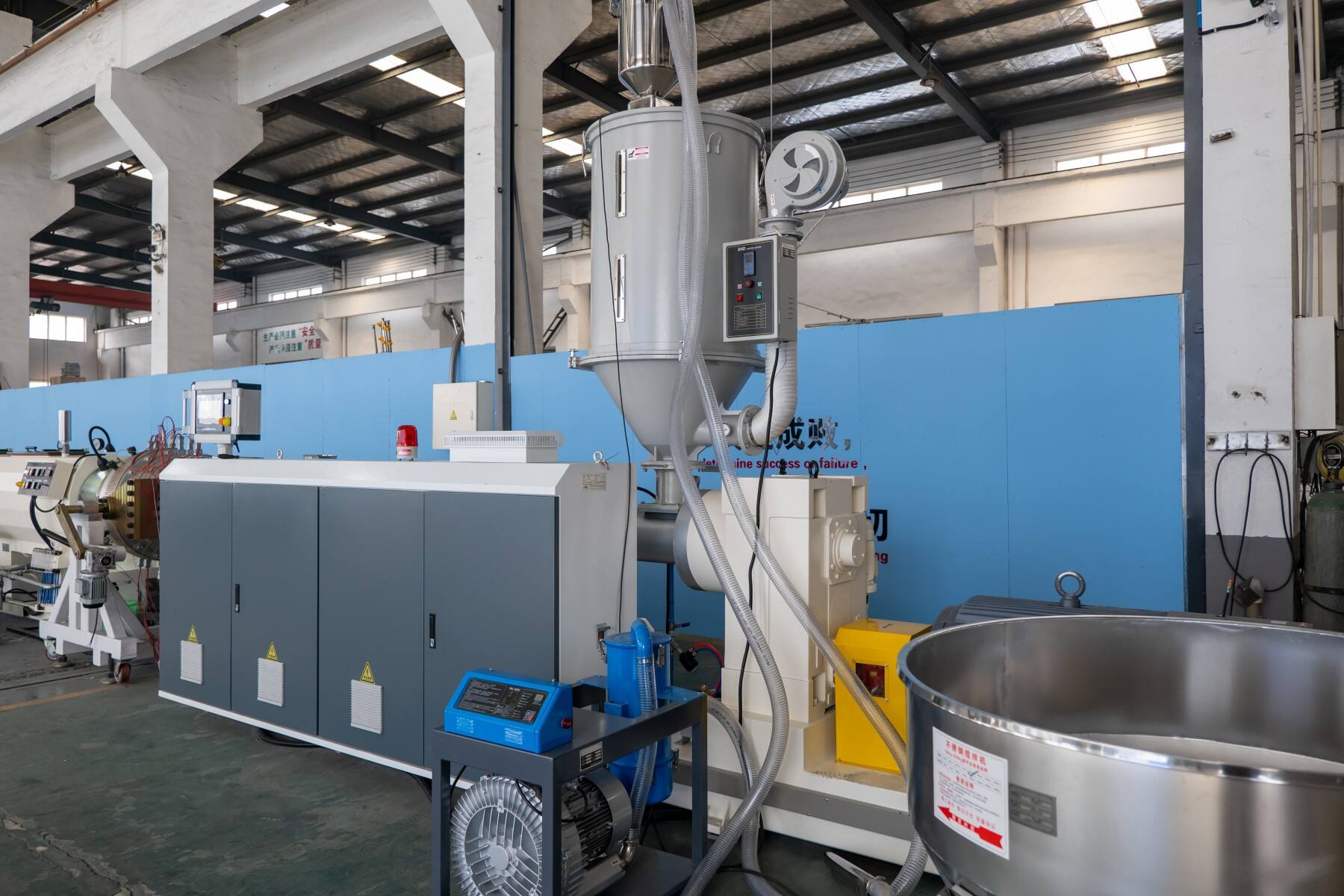

2. Sustainability and Circular Economy Integration
• Energy Recovery and Waste Minimization: PE pipe extrusion lines now incorporate advanced energy recovery systems that repurpose heat generated during the extrusion process for material drying or other functions. This reduces the need for external energy sources and cuts operational costs. Additionally, real-time monitoring systems help minimize material waste by ensuring precise dosing of polyethylene resin, optimizing material use, and reducing scrap production.
• Recycled Material Integration: Many manufacturers are now incorporating recycled polyethylene (rHDPE) into their extrusion lines. By processing post-consumer and post-industrial polyethylene waste, manufacturers reduce their reliance on virgin materials and help mitigate plastic waste. Modern PE extrusion systems are designed to handle recycled materials without compromising the strength or quality of the finished pipes. The ability to blend up to 70% recycled content in non-pressure and selected pressure pipes while maintaining ISO 4427 standards is a significant achievement in sustainability.
• Circular Economy Design Principles: Manufacturers are increasingly designing PE pipes with end-of-life recyclability in mind. For instance, using the same grade of PE for marking stripes ensures that pipes can be easily separated at the end of their life cycle for recycling. Furthermore, several manufacturers have adopted pipe take-back programs, which ensure that old PE pipes are returned to the factory for reprocessing and reuse in new production. This closed-loop approach significantly reduces waste and supports the circular economy.
As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability, the PE pipe extrusion sector is adopting practices aligned with the circular economy model, which focuses on reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling products at the end of their life cycle.
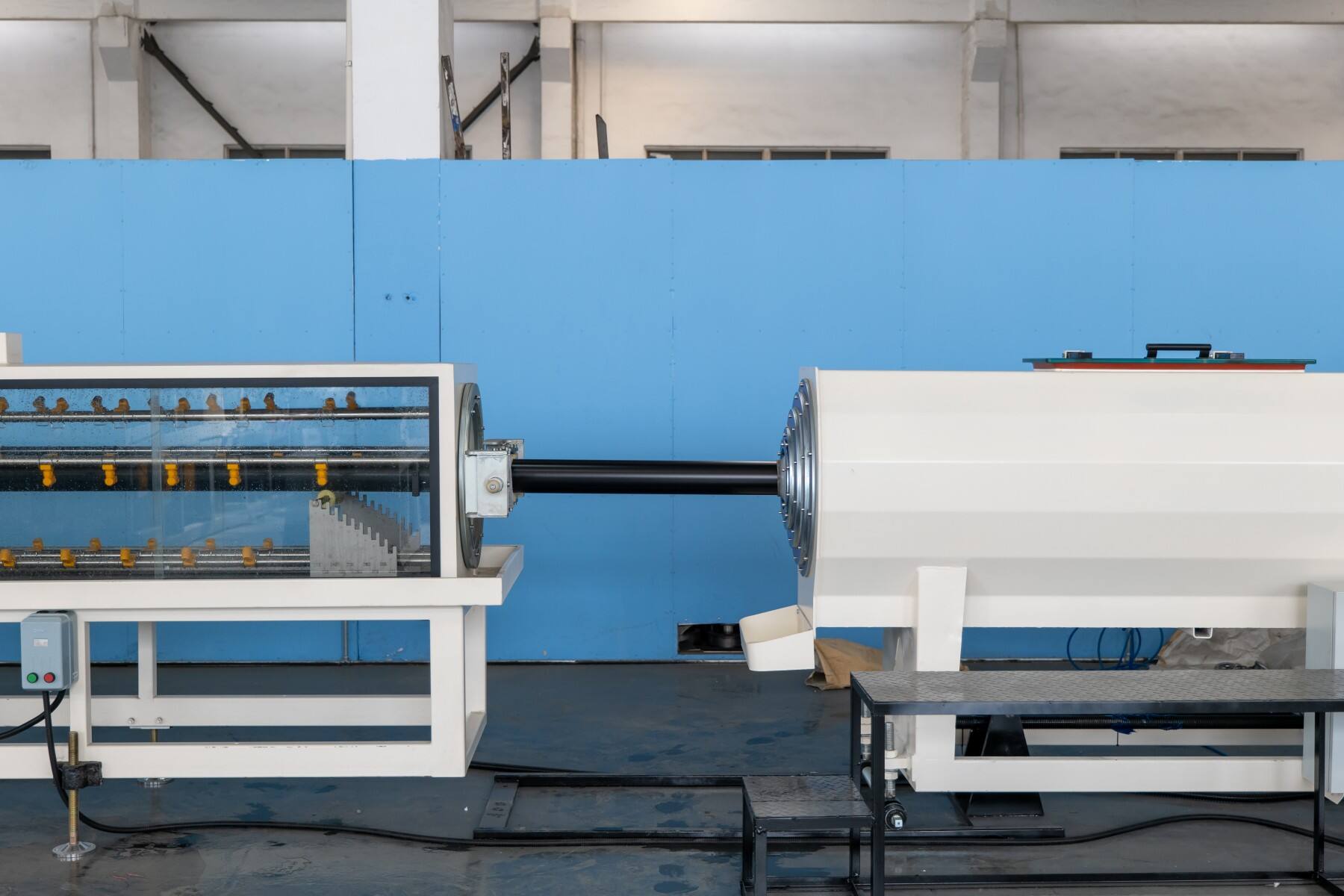

3. Best Practices for Performance Optimization
To achieve peak performance and sustainability, manufacturers must adhere to several best practices:
• Energy Management: Retrofitting all extruder drives to IE5+ motors and integrating variable-speed controls ensures that energy is used efficiently throughout the extrusion process. Zone-specific infrared heating further optimizes energy consumption by heating only the necessary areas of the die head.
• Maximizing Recycled Material Use: To ensure that recycled materials meet the required standards, dedicated drying and decontamination units are essential. These units help remove impurities from recycled polyethylene, ensuring that the material retains its mechanical properties and is suitable for high-quality pipe production.
• Waste Reduction and Process Optimization: Real-time ultrasonic or laser wall-thickness scanners and automatic die-centering systems allow for precision control over pipe dimensions, reducing wall thickness by 3–5% without falling out of tolerance. Start-up scrap is immediately ground and returned to the extruder for reprocessing, ensuring that waste is minimized throughout the production process.
• Predictive Maintenance and Smart Technologies: The integration of IoT sensors on extruders and other critical components helps predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach to maintenance reduces unplanned downtime and helps optimize operational efficiency.
• Operator Excellence and Training: Using VR-based simulators for operator training enables new staff to reach full productivity in days rather than months. Additionally, unified Human-Machine Interface (HMI) systems across the extrusion line reduce human error and improve consistency in production.
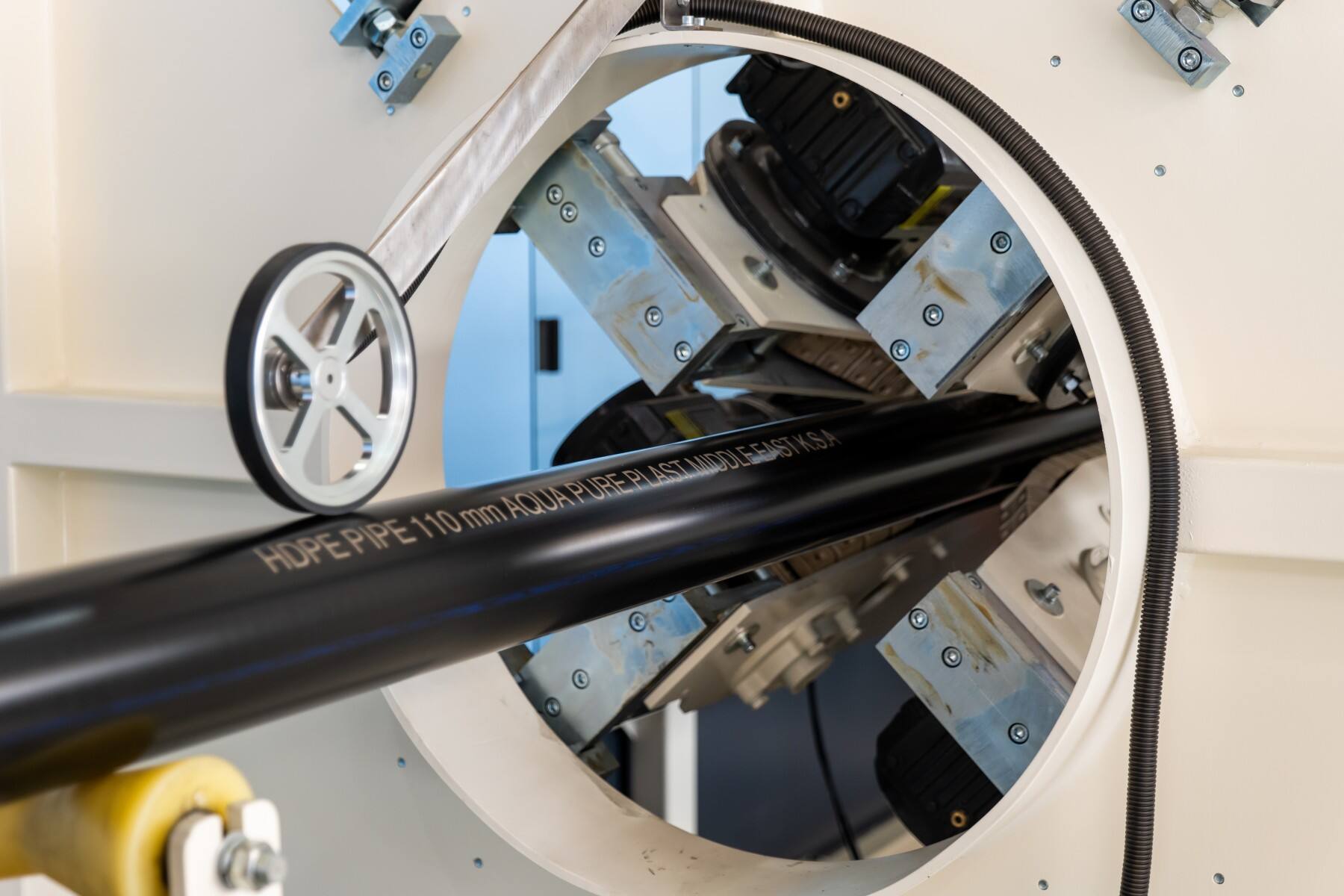

4. Outlook for the Future (2026–2030)
Looking ahead, the PE pipe extrusion industry is poised for further advancements:
• Cradle-to-Cradle Certification: The industry is expected to move towards full cradle-to-cradle carbon-footprint tracking, ensuring that the entire life cycle of PE pipes, from production to disposal, is carbon-neutral.
• Hydrogen-Certified Pipes: The need for hydrogen distribution networks is increasing, and PE100-RC pipes without carbon black, which are detectable by magnetic or GPR methods, are being developed to meet these demands.
• 100% Recycled Content Pipes: By 2030, many PE pipe extrusion lines will be capable of producing 100% recycled-content pipes without compromising performance, in compliance with emerging industry standards like the EU CBAM and ISO 14067.